In the world of statistics, probabilities, and data analysis, the term “p hat” frequently appears. For those new to statistics or looking to deepen their understanding, this article provides a complete overview of what that is, how it is used, and its significance in statistical studies. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or simply curious about the topic, this guide will simplify the concept and its applications.
What is P Hat?
P hat (ôç¦), often written as, represents the sample proportion in statistics. It is a statistical measure used to estimate the proportion of a particular characteristic or outcome in a population based on data collected from a sample.
In simpler terms, p hat is the ratio or percentage of success in a sample. It helps researchers make inferences about the entire population without needing to survey everyone.
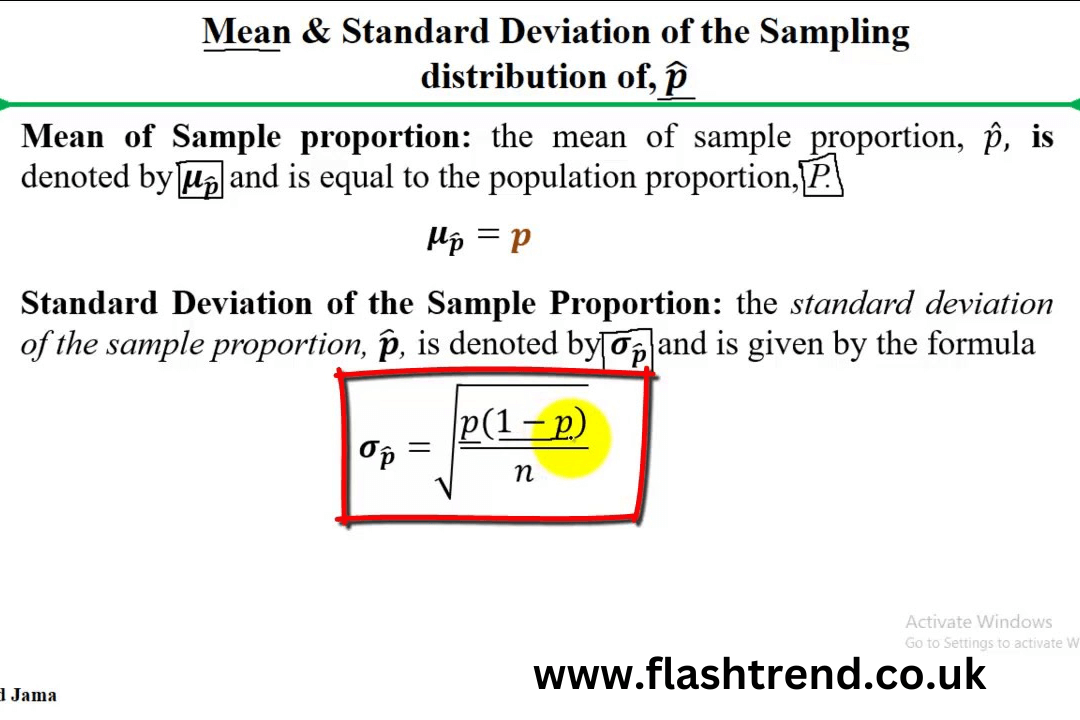
The Formula for P Hat
The formula to calculate phat is straightforward:
Where:
- = Sample proportion (p hat)
- = Number of successes in the sample
- = Total Number of observations or trials in the sample
Example Calculation of P Hat
Let’s say you survey 200 people to find out how many prefer coffee over tea, and 120 respondents choose coffee. Using the formula:
In this case, p hat () equals 0.6, meaning 60% of the surveyed group prefers coffee.
P Hat vs. P: What’s the Difference?
To avoid confusion, it’s essential to understand the difference between p and p hat:
- P (Population Proportion): This is the proper proportion of a characteristic in the entire population. It is often unknown and needs to be estimated.
- P Hat (Sample Proportion): This is the observed proportion based on the sample data. It serves as an estimate of the population proportion.
While p hat approximates p, there’s always a degree of uncertainty because it’s based on a sample, not the entire population.
Applications of P Hat in Statistics
Phat plays a crucial role in various statistical methods and real-world applications. Here are some key areas where it is commonly used:
- Confidence Intervals
P hat is integral to constructing confidence intervals, which provide a range of values within which the proper population proportion (p) is likely to fall. The formula for a confidence interval involving p hat is:
Where:
- = Confidence interval
- = Z-score corresponding to the desired confidence level (e.g., 1.96 for 95%)
- = Sample proportion
- = Sample size
Confidence intervals help researchers understand the reliability of their estimates.
- Hypothesis Testing
In hypothesis testing, p hat is used to test claims or hypotheses about population proportions. For example, if a company claims that 70% of customers are satisfied with their product, researchers can use phat to test this claim with sample data.
The test statistic formula is:
Where:
- = Z-score
- = Sample proportion
- = Population proportion (hypothesized value)
- = Sample size
- Polls and Surveys
Phat is extensively used in polls and surveys to estimate the proportion of people with specific preferences, opinions, or behaviors. For instance, during elections, phat helps estimate the percentage of voters supporting a candidate based on survey data.
- Quality Control
In manufacturing, phat is used to monitor product quality. For example, if a company samples 500 items and finds 25 defective ones, p hat () represents the proportion of defective items in the sample.
Factors Affecting P Hat Accuracy
The accuracy of phat as an estimator of the population proportion depends on several factors:
- Sample Size
Larger sample sizes generally result in more accurate estimates. A small sample size increases the margin of error, making phat less reliable.
- Random Sampling
For phat to accurately reflect the population proportion, the sample must be random and representative. Bias in sampling can lead to inaccurate estimates.
- Variability in the Population
Higher variability in the population can affect the accuracy of phat. If the population proportion is close to 0.5, p hat tends to have more significant variability compared to proportions closer to 0 or 1.
Common Misconceptions About P Hat
- P Hat Equals the True Proportion
While p hat is an estimate of the population proportion, it is not always equal to the actual value. Sampling errors and biases can lead to discrepancies.
- A Larger Sample Always Eliminates the Error
Although larger samples reduce variability, they don’t eliminate sampling error. Confidence intervals account for this uncertainty.
- P Hat Can Exceed 1 or Be Negative
P hat is always between 0 and 1 because it represents a proportion. If calculations yield values outside this range, there’s likely an error in the data or computation.
Practical Tips for Working with P Hat
To ensure accurate and meaningful results when using p hat in statistical analysis, consider the following tips:
- Use Sufficient Sample Sizes
Aim for a sample size large enough to minimize error and increase the reliability of your estimates.
- Avoid Sampling Bias
Ensure your sample is random and representative of the population to avoid skewed results.
- Account for Margin of Error
When interpreting p hat, consider the margin of error and confidence intervals to understand the potential range of values.
- Verify Calculations
Double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy, especially when computing phat, confidence intervals, or test statistics.
Real-Life Examples of P Hat in Action
Example 1: Election Polling
A pollster surveys 1,000 voters to estimate the proportion supporting Candidate A. If 520 respondents express support, phat is:
This means 52% of the sampled voters support Candidate A. Using this phat value; the pollster can construct a confidence interval to estimate the proper proportion in the population.
Example 2: Product Quality Control
A factory inspects 300 products and finds 15 defective items. Phat is:
This indicates that 5% of the sampled products are defective. The factory can use this information to assess overall quality and address potential issues.
Conclusion: Mastering the Concept of P Hat
Understanding phat is essential for anyone working with statistical data. As a fundamental concept, it serves as a cornerstone for estimating population proportions, conducting hypothesis tests, and constructing confidence intervals. By mastering the use of p hat, you’ll be better equipped to analyze data, interpret results, and make informed decisions.
Whether you’re analyzing survey results, conducting quality control, or testing hypotheses, p hat provides a valuable tool for drawing meaningful conclusions from sample data. With the tips and insights provided in this guide, you’re well on your way to becoming proficient in using p hat in your statistical endeavors.
You may also read: The Ultimate Guide to 3 piece suit: Style, Tips, and Trends





